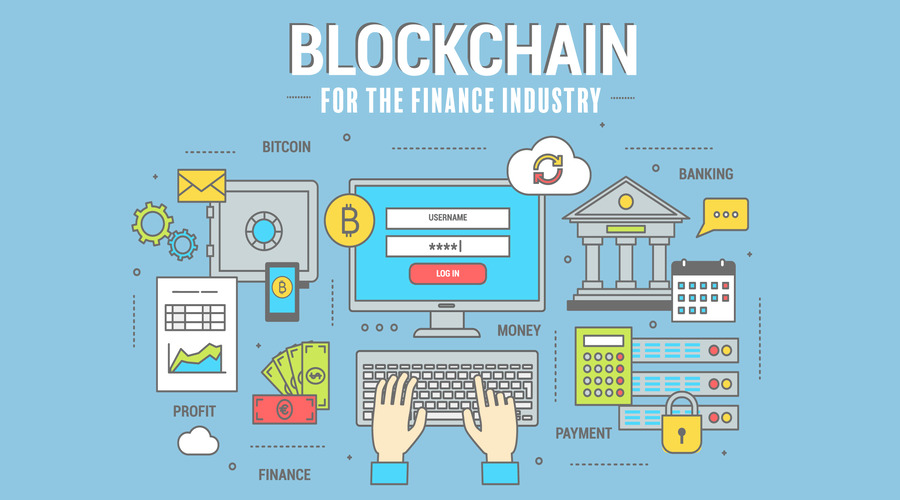
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry, offering increased security, transparency, and efficiency. In this article, we will explore the various applications of blockchain in finance, its benefits, and the challenges faced by its adoption.
Understanding Blockchain in Finance
Blockchain technology is a decentralized ledger system that enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. In the financial industry, blockchain can be used for various applications, including payments, settlements, identity verification, and asset management.
Blockchain in finance can enable faster and more efficient transactions while reducing costs and increasing security. It can also enable greater transparency in financial transactions, making it easier to track and monitor financial activities.
Applications of Blockchain in Finance
Here are some of the most significant applications of blockchain in finance:
Payments and Settlements
Blockchain technology can be used for payments and settlements, enabling fast and secure transactions without the need for intermediaries. This can reduce costs and increase the speed of transactions, making it an attractive option for businesses and individuals looking to conduct financial transactions.
Asset Management
Blockchain technology can be used for asset management, enabling the secure and transparent tracking of assets such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. This can reduce the risk of fraud and increase the efficiency of asset management processes.
Identity Verification
Blockchain technology can be used for identity verification, enabling secure and tamper-proof identity verification. This can help prevent identity theft and fraud, making it a more secure option for financial transactions.
Supply Chain Finance
Blockchain technology can be used for supply chain finance, enabling the secure and transparent tracking of goods and services throughout the supply chain. This can reduce the risk of fraud and increase the efficiency of supply chain financing processes.
Benefits of Blockchain in Finance
Blockchain technology offers several benefits for the financial industry, including:
Increased Security
Blockchain technology offers increased security through cryptographic techniques and decentralization, making it more difficult for hackers to compromise the system.
Greater Efficiency
Blockchain technology can enable faster and more efficient transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries and decreasing the time and cost of transactions.
Increased Transparency
Blockchain technology enables greater transparency in financial transactions, making it easier to track and monitor financial activities.
Challenges in Adopting Blockchain in Finance
While blockchain technology offers several benefits, there are also challenges that need to be addressed for its successful adoption in the financial industry. Some of the challenges include:
Regulatory Framework
The financial industry is heavily regulated, and there are strict guidelines that need to be followed to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards. The lack of a clear regulatory framework for blockchain in finance can hinder its adoption.
Interoperability
The lack of interoperability between different blockchain networks can hinder its adoption in the financial industry, as it can create barriers to the seamless transfer of assets between different networks.
Scalability
The scalability of blockchain technology is still an issue, with current blockchain networks only able to process a limited number of transactions per second. This can hinder its adoption in the financial industry, which requires high transaction volumes.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is an emerging field in the financial industry that utilizes blockchain technology to provide financial services without the need for intermediaries. DeFi applications include lending, borrowing, and trading cryptocurrencies, as well as decentralized exchanges and prediction markets.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central Bank Digital Currencies, or CBDCs, are digital currencies issued by central banks that utilize blockchain technology. CBDCs can offer several benefits, including faster and more efficient payments and reduced costs associated with printing physical currency. However, there are also concerns regarding the impact of CBDCs on financial stability and privacy.
Smart Contracts
Self-executing contracts that are coded on the blockchain are known as Smart Contracts. They can automate various financial transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the time and cost of transactions. Smart contracts can be used for various applications, including insurance, derivatives, and trade finance.
KYC/AML Compliance
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations require financial institutions to verify the identity of their customers and monitor their financial activities for suspicious transactions. Blockchain technology can enable more efficient and secure KYC/AML compliance through the use of decentralized identity management and secure data sharing.
Insurance
Blockchain technology can be used for various applications in the insurance industry, including claims management, fraud detection, and risk assessment. By utilizing blockchain technology, insurance companies can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and provide greater transparency to customers.
Tokenization
Tokenization involves the use of blockchain technology to create digital tokens that represent real-world assets, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. By tokenizing assets, they can be traded and transferred more efficiently and securely, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing transparency in financial transactions.
Data Management
Blockchain technology can be used for secure and efficient data management in the financial industry. By utilizing blockchain technology, financial institutions can securely store and share sensitive financial data, reducing the risk of data breaches and increasing efficiency in data management processes.
International Remittances
Blockchain technology can be used for international remittances, enabling faster and more efficient cross-border transactions. By utilizing blockchain technology, international remittances can be processed more quickly and at a lower cost, reducing the financial burden on individuals and businesses.
Challenges in Adoption
While blockchain technology offers significant benefits for the financial industry, there are also challenges that need to be addressed for its successful adoption. These include regulatory frameworks, interoperability, scalability, and the need for standardization in blockchain technology.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is transforming the financial industry, enabling increased security, transparency, and efficiency in financial transactions. Its applications in finance, including DeFi, CBDCs, smart contracts, KYC/AML compliance, and insurance, offer significant benefits to the financial industry. While challenges such as regulatory frameworks, interoperability, and scalability need to be addressed for its successful adoption, the continued growth and evolution of blockchain technology offer promising opportunities for the future of finance.