As a transactional omni-chain infrastructure network, Mango Network provides an innovative omni-chain bridging protocol solution to solve the problems of asset interest, transaction confirmation delay, lack of smart contracts, and high transaction fees in the Bitcoin network. It also provides cross-chain interoperability for native assets such as Bitcoin, greatly expanding the interaction capabilities of users and various protocols. This groundbreaking technological advancement follows the rising hotspot of the Bitcoin Layer 2 ecosystem, bringing new energy and opportunity to the cryptocurrency market.
Mango Network supports a series of Bitcoin protocols including BRC-20, BRC-420, Atomicals, Pipe, etc., enhancing the liquidity and availability of Bitcoin assets in different blockchain ecosystems. This comprehensive compatibility has made Mango Network a key hub for connecting Bitcoin with traditional smart contract chains such as Ethereum and its Layer 2 solutions, while also providing unprecedented smart contract functionality for non-smart contract chains such as Bitcoin and Dogecoin, greatly expanding their potential applications and market participation.
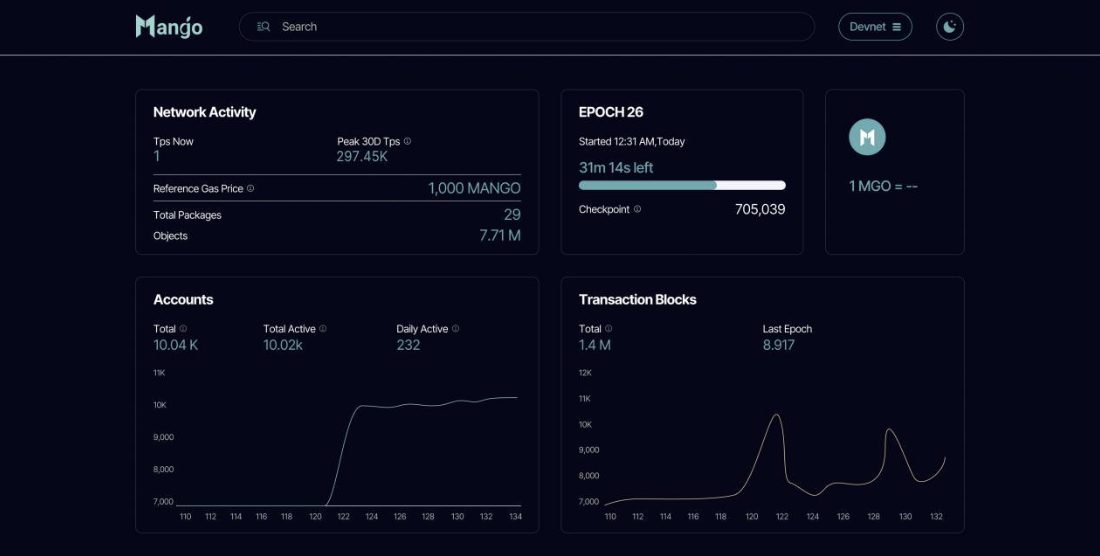
The Layer 1 solution of Mango Network has received strong support from the Move language, providing developers and users with a secure, modular, and high-performance Web3 infrastructure. With a transaction processing speed of up to 297,450 transactions per second (TPS), it demonstrates superior performance while maintaining a high degree of standardization, scalability, and interoperability. This is particularly important in the current Bitcoin Layer 2 ecosystem, as the market’s demand for efficient and low-cost cross-chain solutions is growing rapidly with the rapid development of DeFi and other blockchain applications.
With the support of Mango Network, users can freely transfer their BTC assets into the Mango ecosystem and use them for various DeFi applications without worrying about the security of their assets or the complexity of transactions. This seamless cross-chain experience not only provides new investment and earning opportunities for Bitcoin holders, but also brings more innovation and growth potential to the entire blockchain industry.
The cross-chain bridging capability of Mango Network allows it to connect various blockchains and layers, including Ethereum mainnet, Layer 2 solutions, and Optimism Stack (such as Base). More importantly, Mango Network also supports non-smart contract chains such as Bitcoin, which has achieved unprecedented smart contract functionality for these traditional chains, greatly expanding their potential applications and market participation. In this way, Mango Network not only provides strong support for the cross-chain liquidity of Bitcoin assets, but also makes important contributions to the interoperability of the entire blockchain industry and the development of decentralized finance (DeFi).
1. What is Mango Network – a transactional omni-chain infrastructure network, realizing a comprehensive platform for omni-chain interaction.
Mango Network is a transactional omni-chain infrastructure network that integrates Layer 1 blockchain and smart contract functionality. It has the ability to interact with various blockchains and layers built-in for unified management of assets, data and liquidity across different blockchain ecosystems. The smart contract feature of Mango Network is particularly suitable for blockchains like Bitcoin that do not inherently support smart contracts. Through Mango Network, the assets of these chains can be utilized in the Web3 domain, enabling value transfer.
2. Why mango network was created – bridging blockchain fragmentation
The motivation behind creating Mango Network stems from a deep understanding of the rapid expansion and continuous fragmentation of the cryptocurrency industry. With the rise of DeFi, blockchain gaming, social applications, and more, new blockchains and layers are constantly emerging to meet the demand for speed, flexibility, and low-cost transactions. However, such a diverse ecosystem also brings a series of challenges, including the complexity of cross-chain operations, security issues, and inconsistency in user experience.
Mango Network aims to solve these problems by providing a unified platform that allows users and developers to easily access and interact with different blockchain ecosystems. Through Mango Network, users can manage multiple types of encrypted assets without the need for separate wallets for each blockchain or layer, and without complex cross-chain operations. At the same time, Mango Network has added new application dimensions to traditional chains such as Bitcoin and Dogecoin by providing advanced smart contract functionality, thereby driving innovation and development in the entire industry.
The underlying technology principle of Mango Network is a highly integrated system aimed at achieving seamless interoperability between different blockchains. The core of this technology lies in providing a unified platform that allows assets, data, and smart contracts to freely flow and interact between multiple blockchain networks.
Mango Network omni-chain Technology Architecture Diagram
(1) Multi-chain compatibility: Mango Network has designed a protocol that is compatible with multiple blockchains and layers. It can recognize and process transactions and assets from different blockchain networks such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, Tron, Aptos, and Sui, etc.
(2) Cross-chain bridging: Mango Network uses cross-chain bridging technology to connect different blockchains. These bridges act as intermediaries that allow assets to be transferred from one chain to another while keeping their value and properties intact. Bridging technology is key to enabling cross-chain transactions, ensuring the security and accuracy of asset transfers.
(3) Smart Contract Platform: Mango Network is not only a cross-chain bridging network, but also a smart contract platform. It allows developers to create and deploy smart contracts on the Mango Network, which can be executed on different blockchains, thereby expanding the application scope of smart contracts.
(4) High-performance infrastructure: As a Layer1 solution, Mango Network provides high-performance infrastructure. Its design supports high throughput transaction processing, low latency transaction confirmation, and efficient resource utilization, all of which are necessary for modern blockchain applications.
(5) Security and Decentralization: Mango Network has implemented a series of security measures to protect the network and user assets, inclding encryption technology, multi-signature verification, and offline distributed verification nodes, etc., to ensure the decentralization and resistance to attacks of the network.
(6) User-friendly interface: Mango Network provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to easily engage in cross-chain transactions and manage assets to reduce the user entry barrier, making it convenient for non-technical users to use blockchain services.
Through these technological principles, Mango Network aims to build a comprehensive blockchain ecosystem, supporting cross-chain asset liquidity, and promoting the development of DeFi and other blockchain applications, while providing users with a secure, efficient, and convenient interactive platform.
3. How does the Mango Network omni-chain protocol work?
The operation of the Mango Network’s omni-chain protocol is based on a series of complex technologies and mechanisms, aiming to achieve interoperability and asset liquidity between different blockchains. The core components and operation of the Mango Network’s omni-chain protocol include:
(1) Multi-layer architecture: Mango Network is not just a bottom-layer blockchain, it also serves as a functional layer, connecting different blockchains together. This multi-layer architecture design enables Mango Network to interact with various blockchains and layers, achieving a cross-chain flow of assets and data.
(2) Multi-signature verification node: Mango Network utilizes offline distributed verification nodes to monitor and confirm events on external chains, such as money transfers. These nodes operate independently without a live network connection and ensure the authenticity of events by reaching consensus. Once consensus is reached, these nodes sign to confirm these events to the chain to which they are connected, ensuring the security and consistency of cross-chain transactions.
(3) omni-chain smart contract: The omni-chain smart contract of Mango Network is responsible for handling events from external chains. These smart contracts are able to read data from external chains, execute corresponding logic, and return the results to the external chain. As the only source of truth, the omni-chain smart contract ensures that the state of assets and data remains consistent regardless of which chain they are on.
(4) Cross-chain message transmission: Mango Network allows smart contracts to send data and value between different chains and layers through a cross-chain message transmission mechanism. This process typically involves the unique identifier on the call chain, such as transaction hash or block ID number. In this way, the current on-chain smart contracts can communicate with Relayers on different chains to achieve cross-chain transfer of assets and data.
The Mango Network’s omni-chain protocol achieves seamless connection between different blockchains, providing a solid foundation for asset liquidity and cross-chain applications. This design not only improves the efficiency and security of transactions, but also provides developers and users with a more flexible and convenient cross-chain interaction experience.
4. Bridge security is crucial
Mango Network has carefully designed a comprehensive set of security measures to ensure bridge safety.
First, it uses offline distributed validation nodes, which can independently validate transactions without directly connecting to the network. This means that even in the event of a network attack, these nodes are still able to maintain the integrity and security of transactions.
The multi-signature verification mechanism is another key component of Mango Network’s security. This mechanism requires multiple independent signatures to confirm a transaction, thereby increasing resistance to potentially fraudulent behavior. In the Mango Network, transactions can only be finally processed after being confirmed by multiple validating nodes, ensuring the security and decentralization of the network.
In addition, Security is further enhanced by the Mango Network decentralized proof-of-entitlement network. In this network, no node has sole knowledge or control of the private key, ensuring the security of the private key against the risk of disclosure or misuse.
The Mango Network omni-chain bridging protocol signs and holds assets in their native form, which means that assets always maintain their original state during the transfer process and are not replaced or tampered with. At the same time, idle funds will never be threatened.
The bridging protocol of Mango Network provides a highly secure environment for the safe transmission of data and value through measures such as offline distributed validation nodes, multi-signature verification mechanisms, and decentralized proof-of-stake networks. These measures collectively form the security foundation of the Mango Network bridge, making it a trusted cross-chain solution for users and developers.
The unique feature of Mango Network — a omni-chain technology architecture.
The unique feature of Mango Network lies in its innovative omni-chain technology architecture. It is not only a high-performance Layer 1 platform that provides high-speed transaction processing and rich smart contract functionality, but also enables seamless connection with various blockchain networks, including non-smart contract chains. Through its advanced cross-chain bridging protocol and multi-signature verification mechanism, Mango Network greatly enhances asset liquidity and interoperability while ensuring the security and decentralization of transactions, making Mango Network become a key force driving the development of Web3 and the expansion of the cryptocurrency market.
BTC Bridge Technology Operation Principle
The above diagram shows the operating principle of Mango Network’s BTC Bridge technology, which is a cross-chain bridging mechanism used to transfer and use Bitcoin (BTC) assets within the Mango Network. The following is a logical overview of the mechanism:
(1) Asset transfer: Users first send their BTC assets to the address of the Bridge Relayer, which is a specialized smart contract address used to receive and process cross-chain transfers of BTC.
(2) Offline distributed verification: After receiving BTC, the Bridge Relayer locks the assets and performs multiple verifications. This step involves offline distributed validation nodes that verify and reach a consensus on BTC transfers without relying on real-time network connections.
(3) Multi-signature verification: In order to ensure the security of transactions, Mango Network has adopted a multi-signature verification mechanism. This means that multiple independent signatures are required to confirm the transfer of BTC, thereby increasing security.
(4) Casting 1:1-MBTC: Once BTC is successfully locked and verified, Mango Network will cast an equal amount of MBTC (Mango Bitcoin Token), which is the equivalent token of BTC in Mango Network. This process ensures the authenticity of assets and the consistency of their value.
(5) Asset Distribution: The minted MBTC will be sent to the user’s Mango Network wallet, and users can use these MBTC to participate in lending, GameFi, yield farming pools, liquidity pools, POS staking pools, and other applications within the Mango ecosystem.
(6) Role of Relayer: Throughout the process, the Relayer is responsible for transmitting transaction information and asset status between different chains in the Mango Network. Relayer ensures the accuracy and timeliness of cross-chain communication.
(7) Interaction between Layer 1 and Layer 2: Mango Network, as a Layer 1 blockchain, provides basic security and decentralization. At the same time, it can also interact with Layer 2 solutions (such as Optimism, Arbitrum, etc.) to further expand the application scope of BTC assets.
Through this cross-chain bridging mechanism, Mango Network has achieved the liquidity and availability of BTC assets in different blockchain ecosystems, providing users with a wider range of application scenarios and investment opportunities.
With the support of the Mango network, users can freely transfer their BTC assets into the Mango ecosystem and use them for various DeFi applications without worrying about the security of their assets or the complexity of transactions. This seamless cross-chain experience not only provides new investment and revenue opportunities for Bitcoin holders, but also brings more innovation and growth potential to the blockchain industry as a whole.
The underlying architecture of the Mango network provides these applications with the necessary security, performance, and interoperability, ensuring that users always have control over their assets while also providing an efficient and cost-effective trading experience. The Mango Network will be the key platform to drive the development of Web3 and enable the widespread use of blockchain technology, allowing all participants to enjoy unprecedented freedom and flexibility in the Web3 world.
Mango Network official
Mango Network Dve
- Blockchain Browser: https://mgoscan.com/
- Github:https://github.com/MangoNet-Labs
- GitHub open source: https://github.com/MangoNet-Labs/mango
- Developer Documentation: https://docs.mangonet.io/
- Swap interactive application: https://swap.devnet.mangonetwork.io/swap