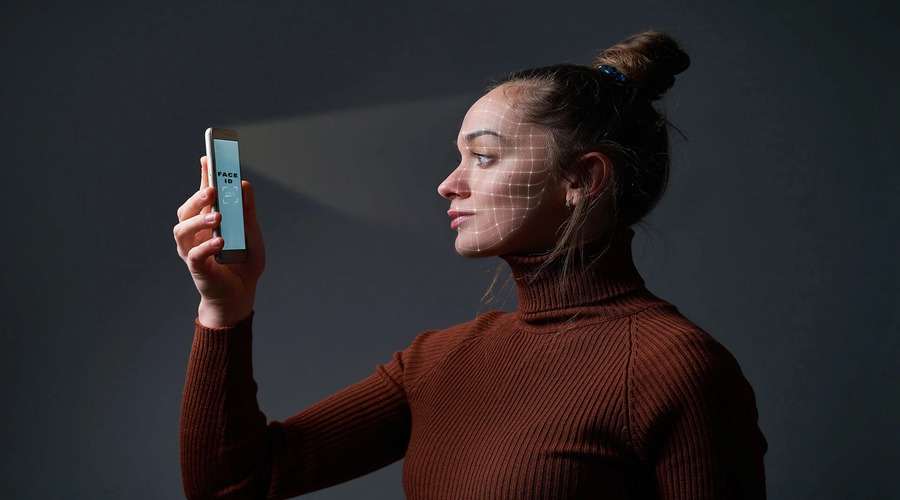
In recent years, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have gained a lot of attention in the art world for their ability to create unique digital ownership of art pieces. However, NFTs have other potential use cases, such as in the creation and authentication of digital identity. With the increasing reliance on digital technologies and the rise of decentralized systems, the role of NFTs in digital identity is becoming more important. In this article, we explore the potential of NFTs in digital identity and how they can revolutionize the way we authenticate and protect our digital identities.
Introduction
The increasing use of digital technologies has brought about new challenges in managing digital identity. With the rise of decentralized systems, there is a need for a secure and reliable method of authenticating and protecting digital identity. NFTs, as unique digital assets that are verified on the blockchain, offer a potential solution to these challenges.
What are NFTs?
NFTs are unique digital assets that are verified on the blockchain. They are created using smart contracts and can represent anything from art pieces to virtual real estate. NFTs are non-fungible, which means that each NFT is unique and cannot be exchanged for another NFT on a one-to-one basis, unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
The Role of NFTs in Digital Identity
Creating Digital Identity
NFTs can be used to create a unique digital identity for individuals. By creating an NFT that represents an individual’s identity, they can verify their ownership of that identity on the blockchain. This can be useful in situations where identity verification is necessary, such as in online transactions or access to secure systems.
Authenticating Digital Identity
NFTs can also be used to authenticate digital identity. By creating an NFT that is linked to an individual’s identity, they can use it to prove their ownership of that identity. This can be useful in situations where identity theft is a concern, as NFTs provide a secure and reliable method of proving ownership of an identity.
Decentralized Identity Systems
NFTs can be used in decentralized identity systems, where individuals can control their own digital identity without relying on centralized authorities. In such systems, individuals can create NFTs that represent their identity, which can be used to verify their ownership of that identity. This can provide a more secure and reliable method of managing digital identity.
The Future of NFTs in Digital Identity
As the use of digital technologies continues to increase, the role of NFTs in digital identity is likely to become more important. NFTs offer a unique solution to the challenges of managing digital identity in a decentralized system. They provide a secure and reliable method of authenticating and protecting digital identity, which can be useful in a variety of contexts.
How to Use NFTs for Digital Identity
- Create an NFT that represents your digital identity. This can be done using a smart contract that is linked to your identity.
- Verify your ownership of the NFT on the blockchain. This can be done by recording the transaction on the blockchain.
- Use the NFT to authenticate your digital identity in online transactions or access to secure systems.
- Store the NFT in a secure location to protect your digital identity from theft or fraud.
Challenges and Risks of Using NFTs for Digital Identity
While NFTs offer a unique solution to the challenges of managing digital identity, there are also some risks and challenges associated with their use. These include:
- Lack of Standardization: There is currently no standardized way of creating NFTs for digital identity, which can make it difficult to ensure their interoperability across different systems.
- Vulnerabilities in Smart Contracts: Smart contracts used to create NFTs can have vulnerabilities that can be exploited by hackers, which can compromise the security of digital identities.
- Dependence on Blockchain: NFTs are dependent on the blockchain for verification, which can create challenges if the blockchain is compromised or becomes unavailable.
- Scalability: The current limitations of blockchain technology can make it difficult to scale NFTs for use in large-scale digital identity systems.
How to Mitigate the Risks of Using NFTs for Digital Identity
- Standardization: The development of standards for creating NFTs for digital identity can help ensure their interoperability across different systems.
- Secure Smart Contracts: Smart contracts used to create NFTs must be developed with security in mind to minimize vulnerabilities that can be exploited by hackers.
- Decentralized Storage: Storing NFTs in a decentralized storage system can help reduce the dependence on blockchain and mitigate the risks of blockchain becoming unavailable.
- Scalability: Advancements in blockchain technology can help address the scalability issues associated with the use of NFTs in large-scale digital identity systems.
- Education: Educating individuals about the risks and benefits of using NFTs for digital identity can help increase awareness and promote responsible use of this technology.
Future Directions for NFTs and Digital Identity
As NFTs continue to gain popularity and their potential use cases expand, there is a need for further research and development to explore their full potential in the context of digital identity. Future directions for NFTs and digital identity include:
- Integration with Decentralized Identity Systems: The integration of NFTs with decentralized identity systems can provide a more secure and reliable method of managing digital identity.
- Standardization and Interoperability: The development of standards for creating NFTs for digital identity can help ensure their interoperability across different systems.
- Advancements in Blockchain Technology: Advancements in blockchain technology can help address the scalability issues associated with the use of NFTs in large-scale digital identity systems.
- New Use Cases: Continued exploration of new use cases for NFTs in digital identity can help unlock their full potential in this field.
NFTs in the Gaming Industry
NFTs have also gained traction in the gaming industry as a way to create unique in-game assets that can be traded and sold on the blockchain. These assets, such as weapons or rare items, can be verified as unique and can have real-world value. In the context of digital identity, NFTs can be used to verify ownership of in-game assets, providing a secure and reliable method of managing digital identity in the gaming world.
NFTs for Identity Verification
NFTs can also be used for identity verification in a variety of contexts, such as online transactions or access to secure systems. By creating an NFT that represents an individual’s identity, they can prove ownership of that identity on the blockchain, providing a secure and reliable method of authentication.
NFTs and Privacy
One potential challenge associated with the use of NFTs in digital identity is privacy. While NFTs can provide a secure and reliable method of managing digital identity, they also have the potential to reveal personal information about individuals if not managed properly. Further research and development are needed to ensure that NFTs are used in a way that protects individuals’ privacy and personal information.
NFTs and Intellectual Property Rights
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are a digital representation of ownership and authenticity of unique digital assets, such as digital art, music, or video. With the rise of NFTs, there has been a growing concern about intellectual property rights in the digital world. Intellectual property rights refer to legal protections that safeguard the rights of creators over their creative works, allowing them to profit from their work and have control over how it is used. While NFTs offer a new way to represent ownership, they do not inherently grant intellectual property rights. Instead, creators must still rely on existing laws and regulations to protect their intellectual property.
One of the benefits of NFTs for intellectual property rights is that they provide a way to prove ownership and authenticity of digital assets, which can be difficult to do otherwise. NFTs can also be used to enforce licensing agreements and control how the asset is used, ensuring that the creator receives proper compensation for their work.
However, there are also some drawbacks to using NFTs for intellectual property rights. For instance, the use of NFTs does not guarantee protection of intellectual property rights, as creators must still rely on existing laws and regulations to protect their work. Additionally, the use of NFTs may also make it easier for others to infringe on intellectual property rights, as it is easier to identify the owner of the asset.
Conclusion
NFTs offer a unique solution to the challenges of managing digital identity in a decentralized system. By creating unique digital assets that are verified on the blockchain, NFTs provide a secure and reliable method of authenticating and protecting digital identity. While there are some risks and challenges associated with their use, advancements in technology and further research can help address these issues. As the use of digital technologies continues to increase, the role of NFTs in digital identity is likely to become more important.











